- Home
- About Us
- Why Choose Us
- Treatments
- Dental Implants
- Root Canal Therapy
- Bridges & Crowns
- Dental Filling
- Teeth Cleaning
- Teeth Whitening
- Dental Veneers
- Tooth Extraction
- Wisdom Tooth Removal
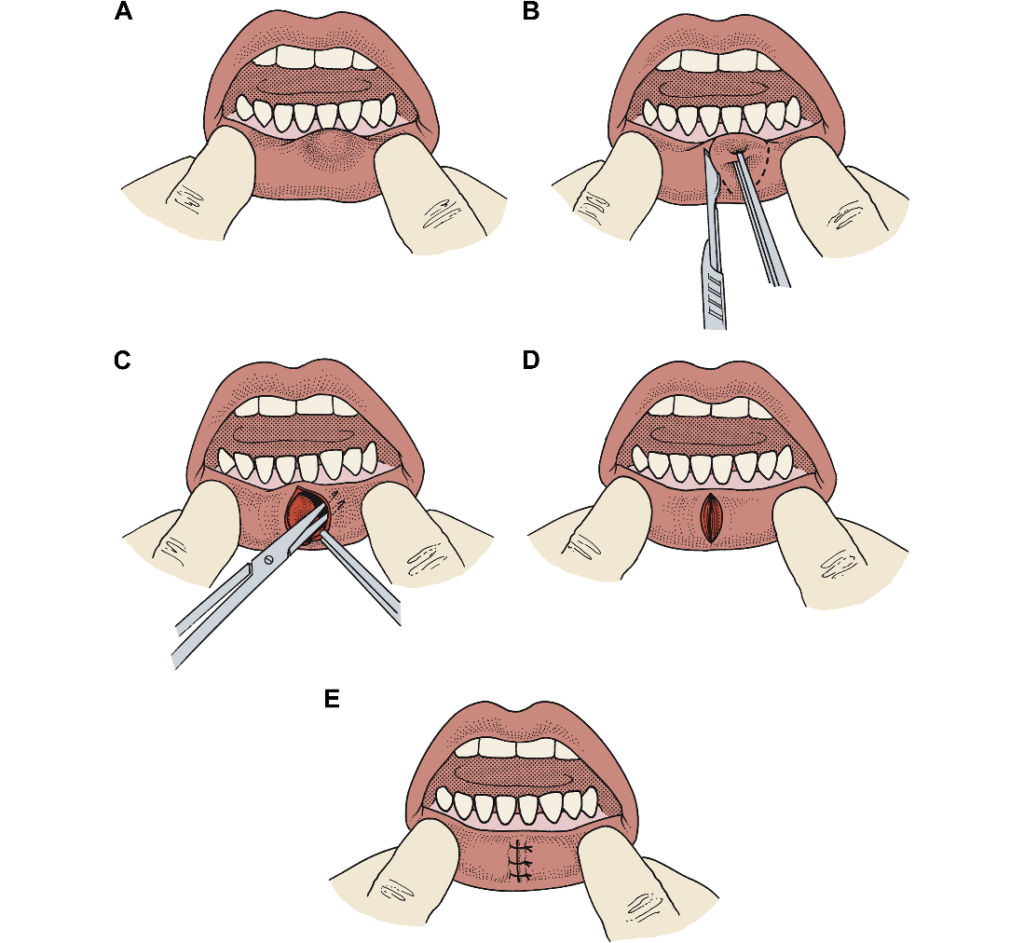
- Cyst Removal
- Child Dental Care
- Periodontal Surgery
- Orthodontics Treatment
- Dental Aligners
- Laser Dentistry
- Biopsy
- TMJ Problem
- Jaw Fracture
- Dentures
- General Anesthesia
- Contact Us